What is KMM?
- Kotlin Multiplatform Mobile is an SDK for Android and iOS development.
- It offers all the benefits of native development while enabling cross-platform apps.
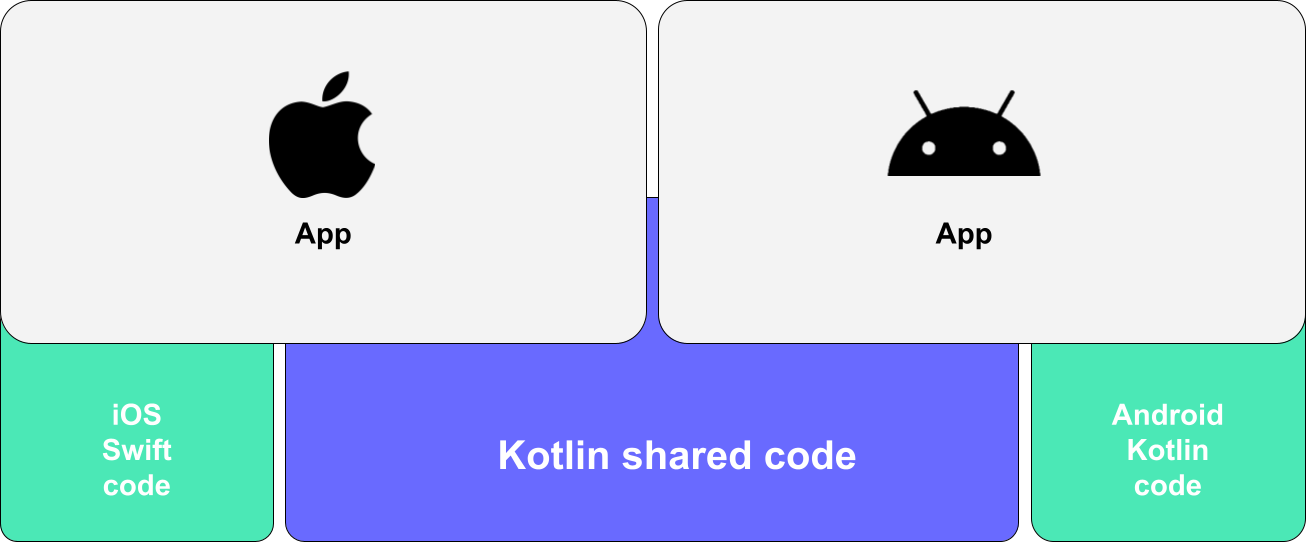
How does it work?
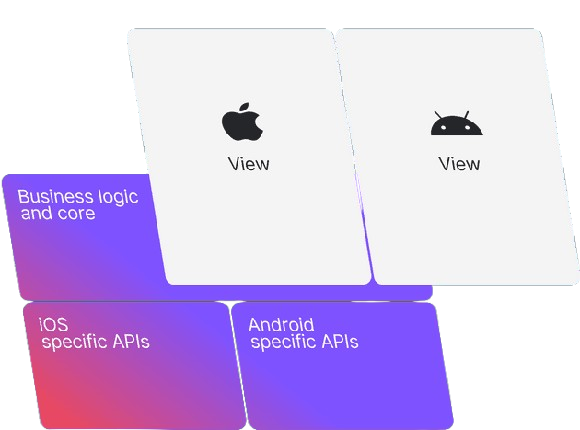
- A KMM app is composed of three modules:
- Android app module: Contains all code to draw and manage the UI, preferably with Jetpack Compose.
- iOS app module: Contains Swift code to draw and manage the UI. The shared module is compiled into an Apple Framework.
- Shared module: Common to both Android and iOS, contains all shared logic (API calls, DB calls, business logic).
Code Structure
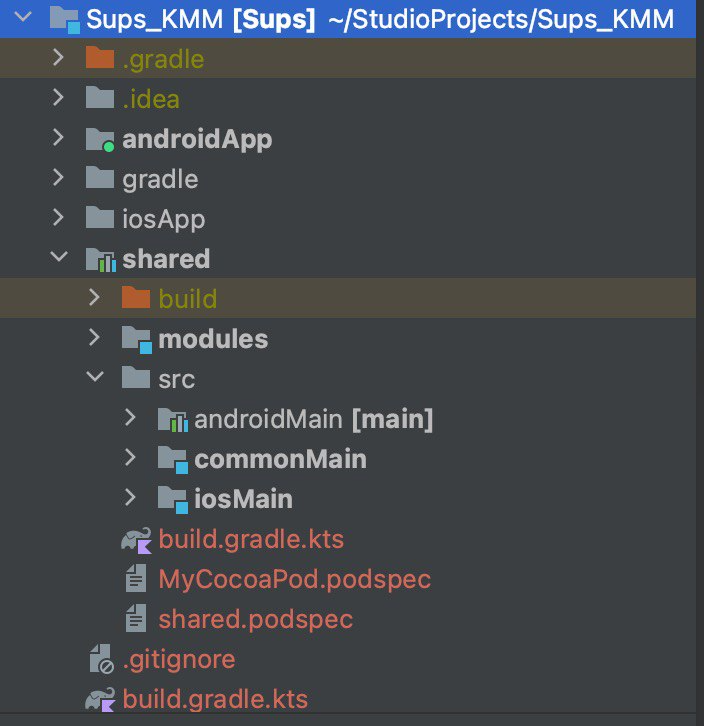
- Project structure includes androidApp, iosApp, and shared modules.
- androidMain: Android-specific code.
- iosMain: iOS-specific code.
- commonMain: Code usable by both platforms.
Project Structure
- A KMM module can be nested by one or many other KMM modules.
- Shared code can be organized in submodules for single functionalities.
- Each submodule is a KMM module with its own androidMain, iosMain, and commonMain sections.

Gradle
- Define all targets and dependencies in Gradle.
- Dependencies of commonMain are inherited by all targets.

androidMain / iosMain
- Platform-specific packages are essential for unique features.
- Preferences, logging, and other platform features must be managed in androidMain and iosMain.
- Use the expect/actual mechanism to manage platform-specific implementations from commonMain.
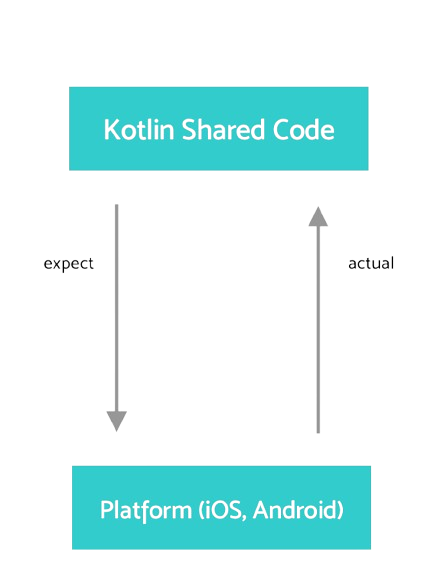
Expect and Actual
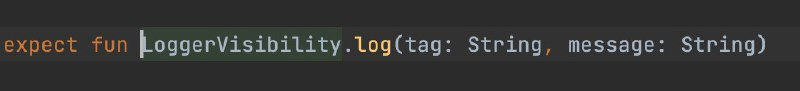
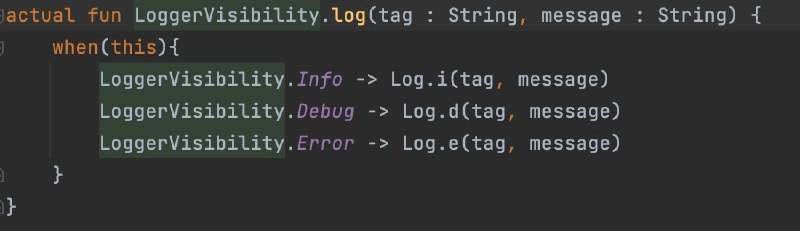
- Mark a method with expect in commonMain to indicate a platform-specific implementation.
- Implement the method in the same package in androidMain and iosMain.
- Example: define
expect fun log()init.eng.loggerand implement in both platforms.

Problems
- Android libraries such as Retrofit and Room are not available on iOS.
- Must-have features: Dependency injection, database, API calls.
- Use expect/actual for platform-specific libraries, but prefer KMM libraries for shared code.
Dependency Injection
- Koin is a KMM dependency usable in the shared module.
- Apps must add Koin dependencies in androidApp and iosApp to configure modules.
- Dagger2 and Hilt are not yet supported, but Google is working on it.
- Custom DI libraries are an alternative for now.
Database and Room
- SQLDelight is the best alternative to Room for KMM projects.
- Integrate dependencies in commonMain, androidMain, and iosMain.
- Configure database name, location, and dialect in Gradle.
Database Implementation
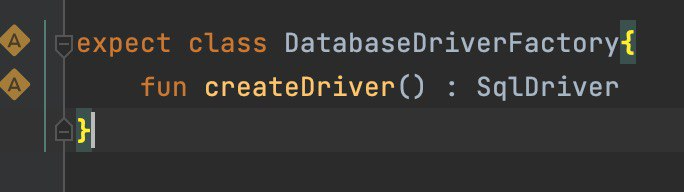
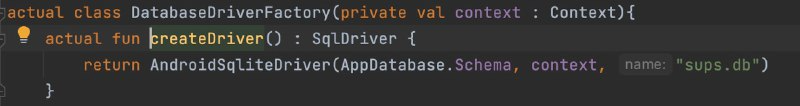
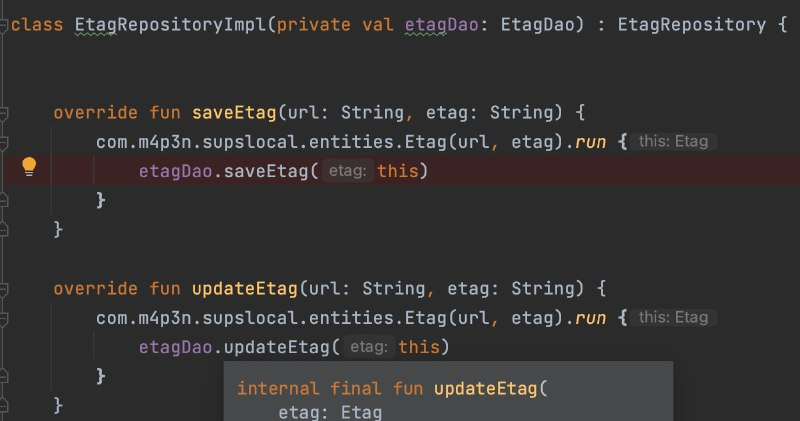
- Write SQL code to generate tables and operations.
- Provide implementations for both systems.
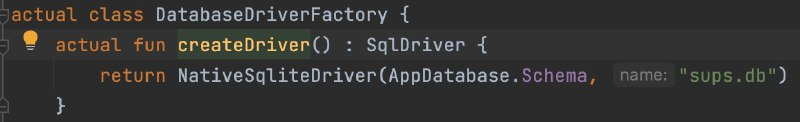
- Use SqlDriver with expect/actual for platform-specific drivers.
- After building, SQLDelight generates AppDatabaseImpl and DAOs for database interaction.

Network Calls and Retrofit
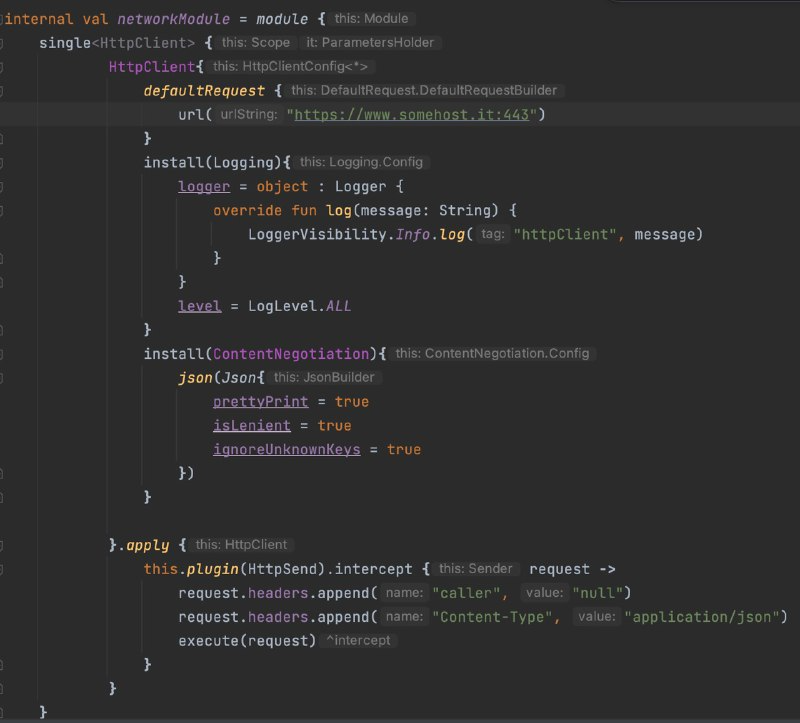
- Retrofit is not available for KMM, but Ktor is a useful library for network calls on both platforms.
- Integrate Ktor dependencies and configure the client with Koin.
Network Implementation
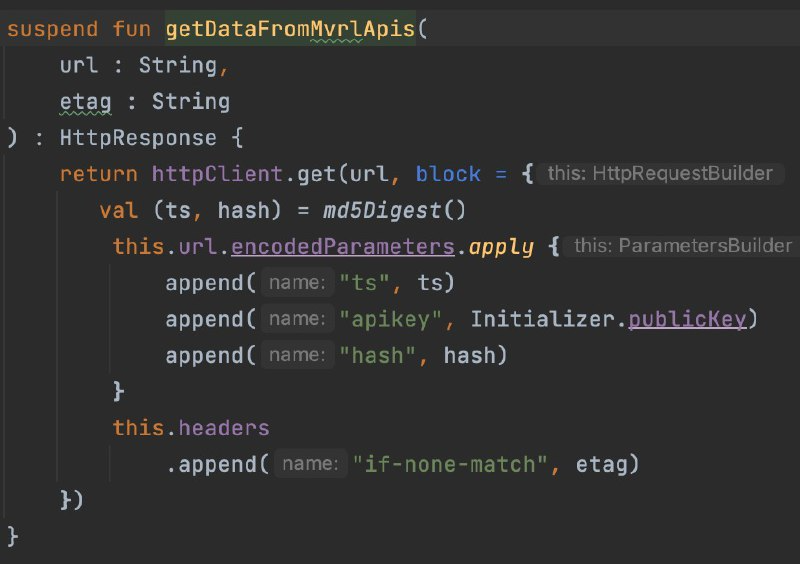
- Make network calls using the configured httpClient (get, post, delete, put).
- Access response as HttpResponse, deserialize body to model.
- Example:
val myModel = Response.body<MyModel>()
Performance Comparison
Below is a test made with the same app, developed in three different ways:
- Android native app with UI based on XMLs, Jetpack, and MVVM.
- Android native app with UI based on Compose, Jetpack, and MVVM.
- Android Kotlin Multiplatform app with Compose.
All apps perform similarly, with some differences:
- App (1): 459 ms to first frame, 79 frames (3.16s) to homepage loaded.
- App (2): 493 ms to first frame, 94 frames (3.76s) to homepage loaded.
- App (3): 604 ms to first frame, 121 frames (4.84s) to homepage loaded.
Tests were made on the same device and network conditions.